In this quick article, we'll have a look at how to list all parent/child nodes in Pandas DataFrame. This might be useful in certain scenarios like verifying trees or networks.
Step 1: Prepare Hierarchical data
Lets prepare hierarchical data which is going to be used for our example:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'parent': [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4],
'child': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9]
})
Sometimes parent or child information might be stored in the index. In those cases index can be transfered to a column by:
df_req['index1'] = df_req.index
Step 2: Install Python package networkx
As a second step we need to install package: networkx by:
pip install networkx
This package is used for creation, manipulation, and analysis of the structure and features of complex networks.
Step 3: Listing Subtree Descendants with NetworkX in Pandas DataFrame
Finally if we like to get all descendants of node 1 in this DataFrame we can do it by converting the DataFrame records to NetworkX nodes:
import networkx as nx
g=nx.DiGraph()
g.add_edges_from(df[['parent', 'child']].to_records(index=False))
and then listing the subtree of NetworkX by:
from networkx.algorithms.traversal.depth_first_search import dfs_tree
x = dfs_tree(g, 1)
x.edges()
Which will result in:
OutEdgeView([(1, 3), (1, 4), (3, 6), (3, 7), (4, 8), (4, 9)])
Visually the same can be represented by:
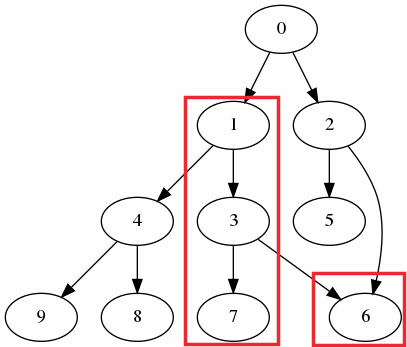
Step 4: Set List of Descendants for each Row(Optional)
In this step we are going to add a new column with a list of all descendants recursively.
def get_descendants(parent):
descendants = list(dfs_tree(g, parent).edges())
return [x[1] for x in descendants]
df["descendants"] = df["parent"].apply(get_descendants)
This will create new column with a list of all childs for the current parent:
| parent | child | descendants | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | [1, 3, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 2, 5, 6] |
| 1 | 0 | 2 | [1, 3, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 2, 5, 6] |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | [3, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9] |
| 3 | 1 | 4 | [3, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9] |
| 4 | 2 | 5 | [5, 6] |
| 5 | 2 | 6 | [5, 6] |
| 6 | 3 | 6 | [6, 7] |
| 7 | 3 | 7 | [6, 7] |
| 8 | 4 | 8 | [8, 9] |
| 9 | 4 | 9 | [8, 9] |
If you like to use custom code version you can use the one below. The code is a bit slower than the previous version:
def get_children(parent_id):
list_of_children = []
def dfs(parent_id):
child_ids = df[df["parent"]==parent_id]["child"]
if child_ids.empty:
return
for child_id in child_ids:
list_of_children.append(child_id)
dfs(child_id)
dfs(parent_id)
return list_of_children
df["descendants"] = df["parent"].apply(get_children)