In this tutorial, we'll see how to solve a common Pandas error – "ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape". We get this error from the Pandas when we try to reindex columns or index objects with duplicate entries.
The error is very common for Pandas methods like:
df.pivot()df.unstack()
There are several quick solutions to it:
(1) Drop duplicates on the index or columns:
df = df.drop_duplicates(['col_1','col_2'])
(2) Use pivot_table:
pd.pivot_table(df, index='col_1', columns='col_2', values=['col_3'] , aggfunc='count')
(3) Use reset the index
.reset_index()
Let's cover several examples explaining the error in more context.
Setup
For this post we will work with the following DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'team': ['team_blue', 'team_red', 'team_blue', 'team_red', 'team_blue', 'team_red', 'team_blue', 'team_red', 'team_blue', 'team_red'],
'day': [7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10],
'points': [10, 12, 9, 7, 14, 5, 9, 8, 10, 11],
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
data:
| team | day | points | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | team_blue | 7 | 10 |
| 1 | team_red | 7 | 12 |
| 2 | team_blue | 8 | 9 |
| 3 | team_red | 8 | 7 |
| 4 | team_blue | 9 | 14 |
Step 1: Detect duplicate records
The error will be raised in case of duplicates on any of the axes.
So in order to ensure that there's no duplicates on the selected columns or rows we can use:
df[df.duplicated(['team', 'day'], keep=False)]
output:
| team | day | points | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | team_blue | 10 | 9 |
| 7 | team_red | 10 | 8 |
| 8 | team_blue | 10 | 10 |
| 9 | team_red | 10 | 11 |
if we get non empty result it means that error will be occur if we try to use those columns with pivot:
pd.pivot(df,'team', 'day' )['points']
The result is Pandas well known error:
ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape
Note: We can use also:
df.duplicated(['row', 'col']).any()
The output is True or False. In case above it's True
Step 2: Remove duplicate records
To solve the error when we have duplicates we can remove duplicates. To do so we will use method: df.drop_duplicates():
df = df.drop_duplicates(['team', 'day'])
This time running:
pd.pivot(df,'team', 'day' )['points']
will not raise errors. The result is:
| day | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| team | ||||
| team_blue | 10 | 9 | 14 | 9 |
| team_red | 12 | 7 | 5 | 8 |
Step 3: Use pivot_table
For duplicated records we can use the method pivot_table with aggregation functions. For example we can check number of records per each group by:
pd.pivot_table(df, index='day', columns='team', values=['points'] , aggfunc='count')
Instead of error we get the count for each column:
| points | ||
|---|---|---|
| team | team_blue | team_red |
| day | ||
| 7 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 |
| 10 | 2 | 2 |
Two main differences between:
pivotand
pivot_table
(1) "pivot_table" is a generalization of "pivot" that can handle duplicate values for index/column pair.
(2) "pivot_table" will only allow numeric types as "values=", whereas "pivot" will take string types.
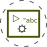
Step 4: Use reset_index
Depending on the data and the expected result we can use multiple transformations to solve the error.
Let's demonstrate that with using method reset_index():
df_agg = df.groupby(by=['team', 'day'])['points'].sum().reset_index()
df_agg.pivot(index='team', columns='day', values=['points'])
The output is:
| points | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| day | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| team | ||||
| team_blue | 10 | 9 | 14 | 19 |
| team_red | 12 | 7 | 5 | 19 |
How does it work?
First we group by the two columns - 'team', 'day' and then calculate the sum() of points for each group.
df.groupby(by=['team', 'day'])['points'].sum()
The result is a pandas Series:
team day
team_blue 7 10
8 9
9 14
10 19
team_red 7 12
8 7
9 5
10 19
Name: points, dtype: int64
reset_index() convert it to a DataFrame without duplicates:
| points | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| day | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| team | ||||
| team_blue | 10 | 9 | 14 | 19 |
| team_red | 12 | 7 | 5 | 19 |
Now we can do pivot() without getting an error: "ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape".
The same result might be achieved in different ways. Depending on the context we can use different methods.
Conclusion
To sum up, this article shows how removing duplicates can solve the "ValueError: Index contains duplicate entries, cannot reshape" error.
We also covered how to find the reasons for the error. Finally we show alternative ways to get the same result.