In this tutorial, we'll learn how to normalize columns or the whole DataFrame in Pandas. We will show different ways like:
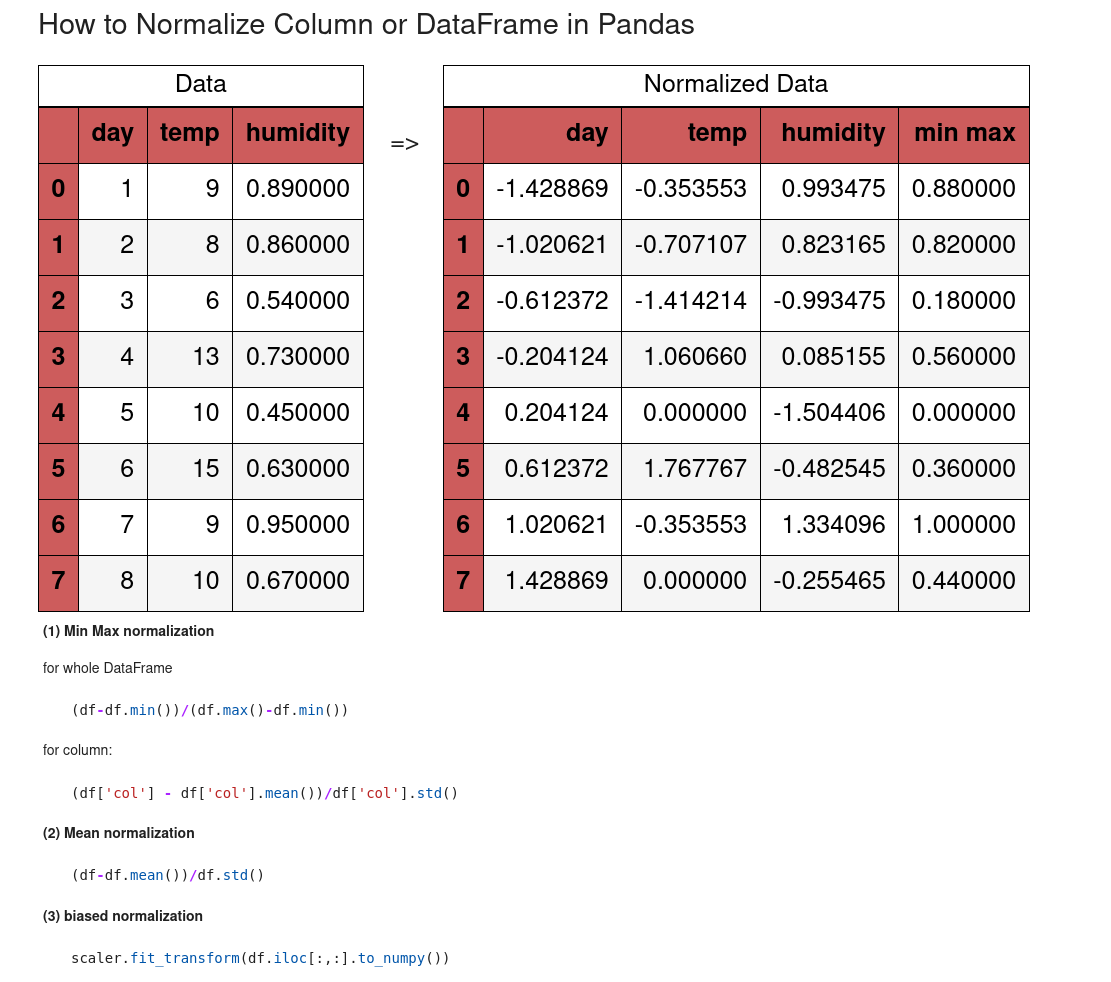
(1) Min Max normalization
for whole DataFrame
(df-df.min())/(df.max()-df.min())
for column:
(df['col'] - df['col'].mean())/df['col'].std()
(2) Mean normalization
(df-df.mean())/df.std()
(3) biased normalization
scaler.fit_transform(df.iloc[:,:].to_numpy())
Let's cover all examples in more detail.
Setup
For this post we are creating example DataFrame with 3 numeric columns:
import pandas as pd
data = {'day': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
'temp': [9, 8, 6, 13, 10, 15, 9, 10],
'humidity': [0.89, 0.86, 0.54, 0.73, 0.45, 0.63, 0.95, 0.67]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data)
Data looks like:
| day | temp | humidity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 9 | 0.89 |
| 1 | 2 | 8 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 3 | 6 | 0.54 |
| 3 | 4 | 13 | 0.73 |
| 4 | 5 | 10 | 0.45 |
1: Min Max normalization in Pandas
So let's start by min max normalization (called also min max scaling) in Pandas and Python.
Single column
To do min max scaling for a single column we can do:
(df['humidity']-df['humidity'].min())/(df['humidity'].max()-df['humidity'].min())
The result is normalized Series:
0 0.88
1 0.82
2 0.18
3 0.56
4 0.00
5 0.36
6 1.00
7 0.44
Name: humidity, dtype: float64
Checking data next to the original column:
| humidity_norm | humidity | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.88 | 0.89 |
| 1 | 0.82 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 0.18 | 0.54 |
| 3 | 0.56 | 0.73 |
| 4 | 0.00 | 0.45 |
All columns
To normalize all columns of a DataFrame we can use:
(df-df.min())/(df.max()-df.min())
Which will result into:
| day | temp | humidity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000000 | 0.333333 | 0.88 |
| 1 | 0.142857 | 0.222222 | 0.82 |
| 2 | 0.285714 | 0.000000 | 0.18 |
| 3 | 0.428571 | 0.777778 | 0.56 |
| 4 | 0.571429 | 0.444444 | 0.00 |
2: Mean normalization in Pandas
Next we can see how to do mean normalization in Pandas and Python.
Single column
For a single column we can apply mean normalization by:
(df['humidity'] - df['humidity'].mean())/df['humidity'].std()
The result and the original values:
| humidity_norm | humidity | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.993475 | 0.89 |
| 1 | 0.823165 | 0.86 |
| 2 | -0.993475 | 0.54 |
| 3 | 0.085155 | 0.73 |
| 4 | -1.504406 | 0.45 |
All columns
To normalize the whole DataFrame with mean normalization we can do:
(df-df.mean())/df.std()
result:
| day | temp | humidity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.428869 | -0.353553 | 0.993475 |
| 1 | -1.020621 | -0.707107 | 0.823165 |
| 2 | -0.612372 | -1.414214 | -0.993475 |
| 3 | -0.204124 | 1.060660 | 0.085155 |
| 4 | 0.204124 | 0.000000 | -1.504406 |
3: Biased normalization in Pandas
To perform biased normalization in Pandas we can use the library sklearn. The results will differ from the Pandas normalization.
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit_transform(df.to_numpy())
The results are:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.527525 | -0.377964 | 1.062070 |
| 1 | -1.091089 | -0.755929 | 0.880001 |
| 2 | -0.654654 | -1.511858 | -1.062070 |
| 3 | -0.218218 | 1.133893 | 0.091035 |
| 4 | 0.218218 | 0.000000 | -1.608277 |
4: Normalize rows in Pandas
There are multiple ways to normalize rows:
- per sum
- mean
- min max
Normalize rows by their sum
To normalize row based on the sum of the row in Pandas we can do:
df.div(df.sum(axis=1), axis=0)
which will give use:
| day | temp | humidity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.091827 | 0.826446 | 0.081726 |
| 1 | 0.184162 | 0.736648 | 0.079190 |
| 2 | 0.314465 | 0.628931 | 0.056604 |
| 3 | 0.225606 | 0.733221 | 0.041173 |
| 4 | 0.323625 | 0.647249 | 0.029126 |
Transpose
To normalize row wise in Pandas we can combine:
.Tto transpose rows to columnsdf.valuesto get the values as numpy array
Let's see an example:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import preprocessing
data = df.T.values
scaler = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
pd.DataFrame(scaler.fit_transform(data)).T
So after using df.values we get:
array([[0.0135635 , 1. , 0. ],
[0.15966387, 1. , 0. ],
[0.45054945, 1. , 0. ],
[0.26650367, 1. , 0. ],
[0.47643979, 1. , 0. ],
[0.3736952 , 1. , 0. ],
[0.7515528 , 1. , 0. ],
[0.78563773, 1. , 0. ]])
which are transformed to:
array([[0. , 0.33333333, 0.88 ],
[0.14285714, 0.22222222, 0.82 ],
[0.28571429, 0. , 0.18 ],
[0.42857143, 0.77777778, 0.56 ],
[0.57142857, 0.44444444, 0. ],
[0.71428571, 1. , 0.36 ],
[0.85714286, 0.33333333, 1. ],
[1. , 0.44444444, 0.44 ]])
Conclusion
In this article we learned how to normalize columns and DataFrame in Pandas. Different ways of normalization were covered like - biased, unbiased, normalization per sum.
We also saw how to normalize rows of a DataFrame. Normalizing data is very useful in machine learning and visualizing data.