In this short guide, we're going to merge multiple CSV files into a single CSV file with Python. We will also see how to read multiple CSV files - by wildcard matching - to a single DataFrame.
The code to merge several CSV files matched by pattern to a file or Pandas DataFrame is:
import glob
for f in glob.glob('file_*.csv'):
df_temp = pd.read_csv(f)
Setup
Suppose we have multiple CSV files like:
- file_202201.csv
- file_202202.csv
- file_202203.csv
into single CSV file like: merged.csv
1: Merge CSV files to DataFrame
To merge multiple CSV files to a DataFrame we will use the Python module - glob. The module allow us to search for a file pattern with wildcard - *.
import pandas as pd
import glob
df_files = []
for f in glob.glob('file_*.csv'):
df_temp = pd.read_csv(f)
df_files.append(df_temp)
df = pd.concat(df_files)
How does the code work?
- All files which match the pattern will be iterated in random order
- Temporary DataFrame is created for each file
- The temporary DataFrame is appended to list
- Finally all DataFrames are merged into a single one
2: Read CSV files without header
To skip the headers for the CSV files we can use parameter: header=None
read_csv('file_*.csv', header=None)
To add the headers only for the first file we can:
- read the first file with headers
- drop duplicates (keep first)
- set column names
All depends on the context.
3: Read sorted CSV files
Module glob reads files without order. To ensure the correct order of the read CSV files we can use sorted:
sorted(glob.glob('file_*.csv'))
This ensures that the final output CSV file or DataFrame will be loaded in a certain order.
Alternatively we can use parameters: ignore_index=True, , sort=True for Pandas method concat:
merged_df = pd.concat(all_df, ignore_index=True, sort=True)
4: Change CSV separator
We can control what is the separator symbol for the CSV files by using parameter:
sep = '\t'
Default one is comma.
5: Keep trace of CSV files
If we like to keep trace of each row loaded - from which CSV file is coming we can use: df_temp['file'] = f.split('/')[-1]:
This will data a new column to each file with trace - the file name origin.
6: Merge CSV files to single with Python
Finally we can save the result into a single CSV file from Pandas Dataframe by:
df_merged.to_csv("merged.csv")
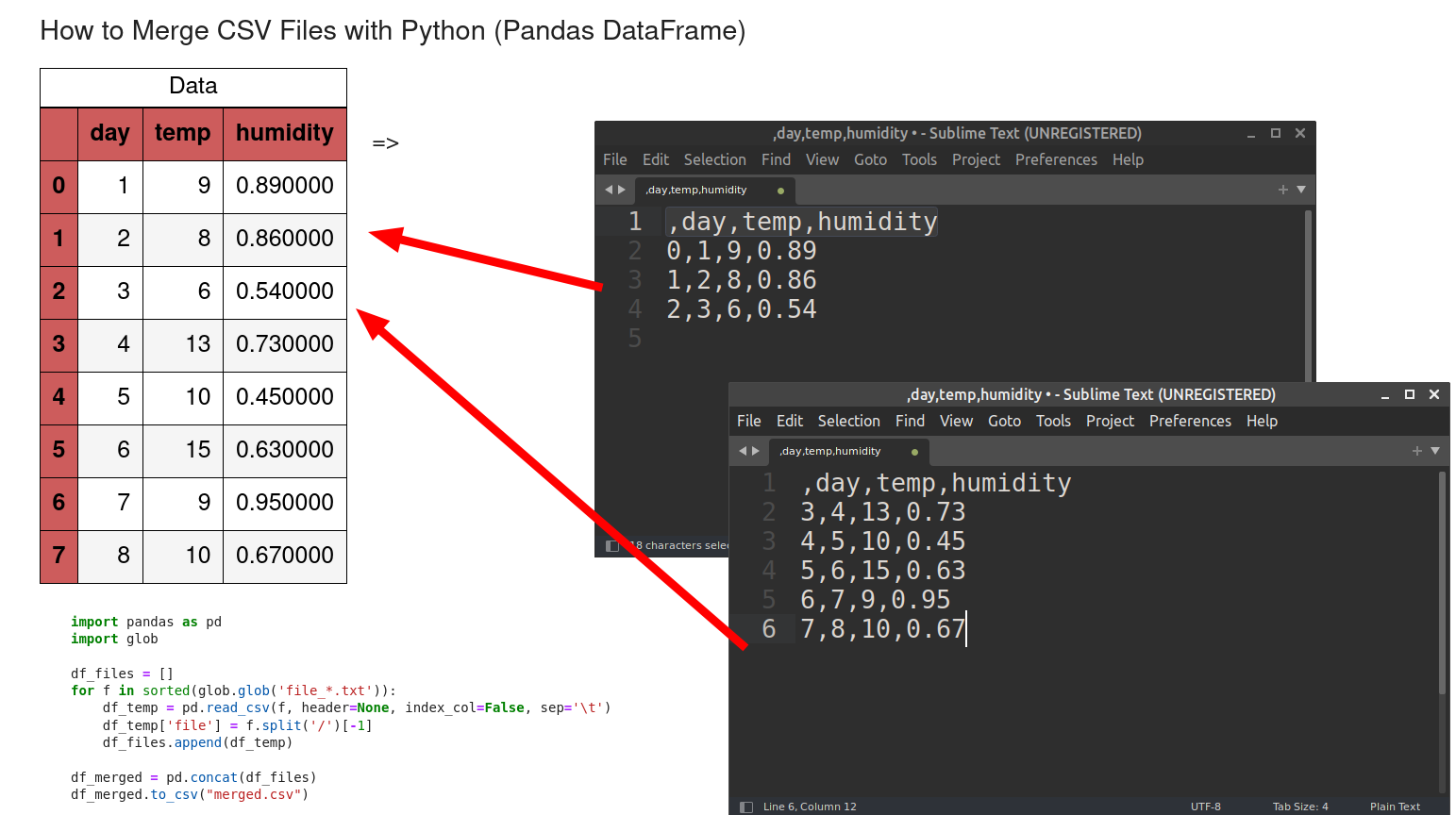
7. Full Code
Finally we can find the full example with most options mentioned earlier:
import pandas as pd
import glob
df_files = []
for f in sorted(glob.glob('file_*.txt')):
df_temp = pd.read_csv(f, header=None, index_col=False, sep='\t')
df_temp['file'] = f.split('/')[-1]
df_files.append(df_temp)
df_merged = pd.concat(df_files)
df_merged.to_csv("merged.csv")
Conclusion
We saw how to read multiple CSV files with Pandas and Python. Different options were covered like:
- changing separator for
read_csv - keeping trace of the source file
- sorting files in certain order
- skipping headers