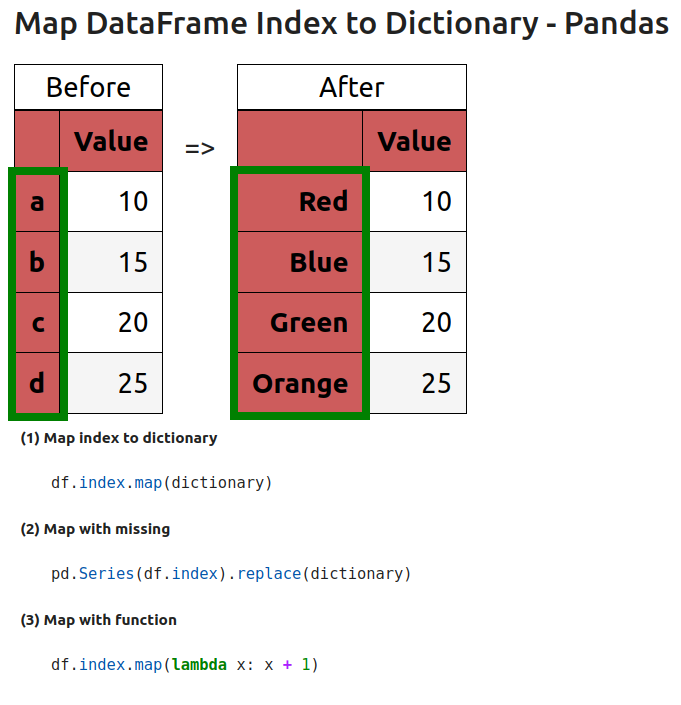
In this post, we'll explore how to map DataFrame Index values using a dictionary in Pandas.
Setup
Consider a DataFrame with following data:
import pandas as pd
data = {'Value': [10, 15, 20, 25]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=[1,2,3,4])
result:
| Value | |
|---|---|
| 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 15 |
| 3 | 20 |
| 4 | 25 |
This will create a DataFrame with an index labeled 1, 2, 3 and 4.
1: Map index with df.index.map
To map DataFrame index with Python dictionary we can use method: df.index.map:
index_mapping = {1: 'Red', 2: 'Blue', 3: 'Green', 4: 'White' }
df.index = df.index.map(index_mapping)
The new index is based on the mapping of the provided values in the dictionary:
| Value | |
|---|---|
| Red | 10 |
| Blue | 15 |
| Green | 20 |
| White | 25 |
2: Map with a function
To map Pandas index with a function we have two options:
- lambda
- predefined functions
lambda
Let's remind us that - lambda function is a small anonymous function.
df.index.map(lambda x: x + 1)
the result is new index with changed values:
Index([2, 3, 4, 5], dtype='int64')
Another lambda example to map index:
df.index.map(lambda x: x.upper())
predefined functions
The example below will map all values and format the them:
df.index.map('Index {}'.format)
the result is new index with changed values:
Index(['Index 1', 'Index 2', 'Index 3', 'Index 4'], dtype='object')
3: Missing values in the dict
There is a parameter na_action which controls behavior of missing values. If the index contains missing values they could be exclude from mapping with function:
import pandas as pd
data = {'Value': [10, 15, 20, 25]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=[1,2,3, None])
df.index.map('Index {}'.format, na_action='ignore')
Will result into:
Index(['Index 1.0', 'Index 2.0', 'Index 3.0', nan], dtype='object')
4: Map with values without mapping
If a value is not found in the index we will end with index full of NaN values:
index_mapping = {1: 'Red', 2: 'Blue'}
df.index = df.index.map(index_mapping)
result:
| Value | |
|---|---|
| Red | 10 |
| Blue | 15 |
| NaN | 20 |
| NaN | 25 |
To avoid that we can use method replace:
index_mapping = {1: 'Red', 2: 'Blue'}
df.index = pd.Series(df.index).replace(index_mapping)
Conclusion
Mapping a DataFrame index using a dictionary might help to control index values. Some use cases are:
- data cleaning
- memory efficiency
- anonymization