In this short guide, I'll show you how to combine separate Date and Time columns into a single DateTime column in Pandas.
When working with datasets, dates and times are often stored separately. Merging them into a single column can help with time-series analysis, sorting, and filtering.
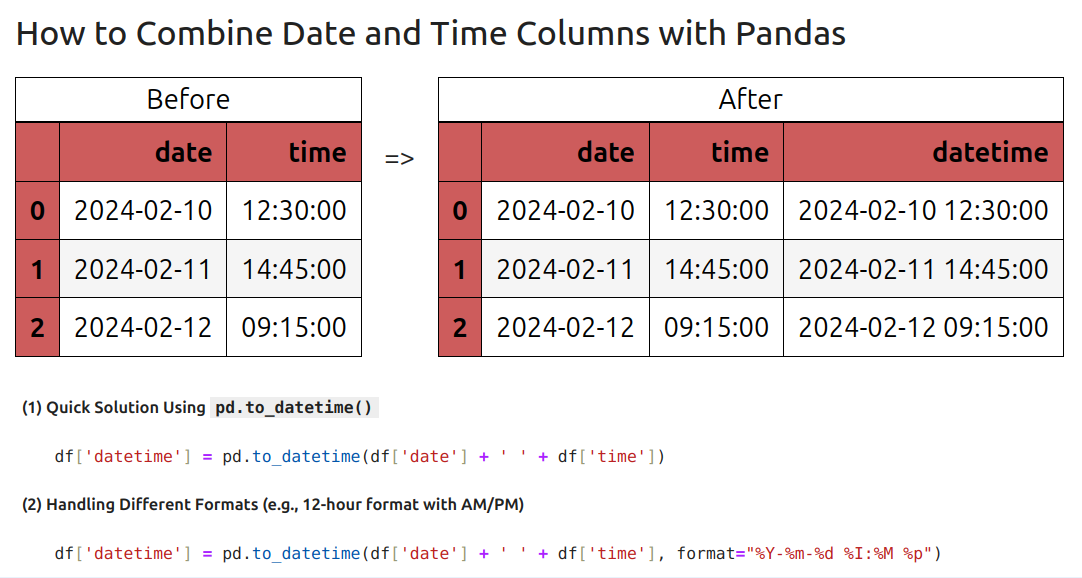
(1) Quick Solution Using pd.to_datetime()
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'] + ' ' + df['time'])
(2) Handling Different Formats (e.g., 12-hour format with AM/PM)
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'] + ' ' + df['time'], format="%Y-%m-%d %I:%M %p")
1: Example of Separate Date and Time Columns
Let’s say we have a dataset with two columns: date and time:
import pandas as pd
# Sample data
data = {
'date': ['2024-02-10', '2024-02-11', '2024-02-12'],
'time': ['12:30:00', '14:45:00', '09:15:00']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Output:
| date | time | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2024-02-10 | 12:30:00 |
| 1 | 2024-02-11 | 14:45:00 |
| 2 | 2024-02-12 | 09:15:00 |
2: Combine Date and Time into DateTime Column
To merge them, we can use pd.to_datetime():
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'] + ' ' + df['time'])
Output:
| date | time | datetime | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2024-02-10 | 12:30:00 | 2024-02-10 12:30:00 |
| 1 | 2024-02-11 | 14:45:00 | 2024-02-11 14:45:00 |
| 2 | 2024-02-12 | 09:15:00 | 2024-02-12 09:15:00 |
The new column datetime is now in DateTime format, which allows for easier manipulation and analysis.
3: Handling Different Formats
If your dataset has different date or time formats, Pandas can automatically parse them, or you can specify a format:
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'] + ' ' + df['time'], format="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
For a 12-hour format with AM/PM, use:
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'] + ' ' + df['time'], format="%Y-%m-%d %I:%M %p")
Conclusion
In this guide, we covered how to:
- Merge separate
dateandtimecolumns - Convert them into a single DateTime column
- Handle different time formats
This method is useful when working with time-based datasets, logs, and time-series analysis.