In this short guide, I'll show you how to create a new count column based on value_counts from another column in Pandas DataFrame.
There are multiple ways to count values and add them as new column:
(1) value_counts and map
counts = df['col1'].value_counts()
df['col_count'] = df['col1'].map(counts)
(2) group by and transform
df['col_count'] = df.groupby(['col1'])['col1'].transform('count')
You can also read the tricky related topic: How to Group by multiple columns, count and map in Pandas .
In addition we will answer on these questions:
- How do I count values in a new column in pandas?
- How do I create a new column based on another column value in pandas?
- How do I count values in one column based on another column?
Let's discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both of them in a few examples.
Setup
Let's create a sample DataFrame to count values in it's columns:
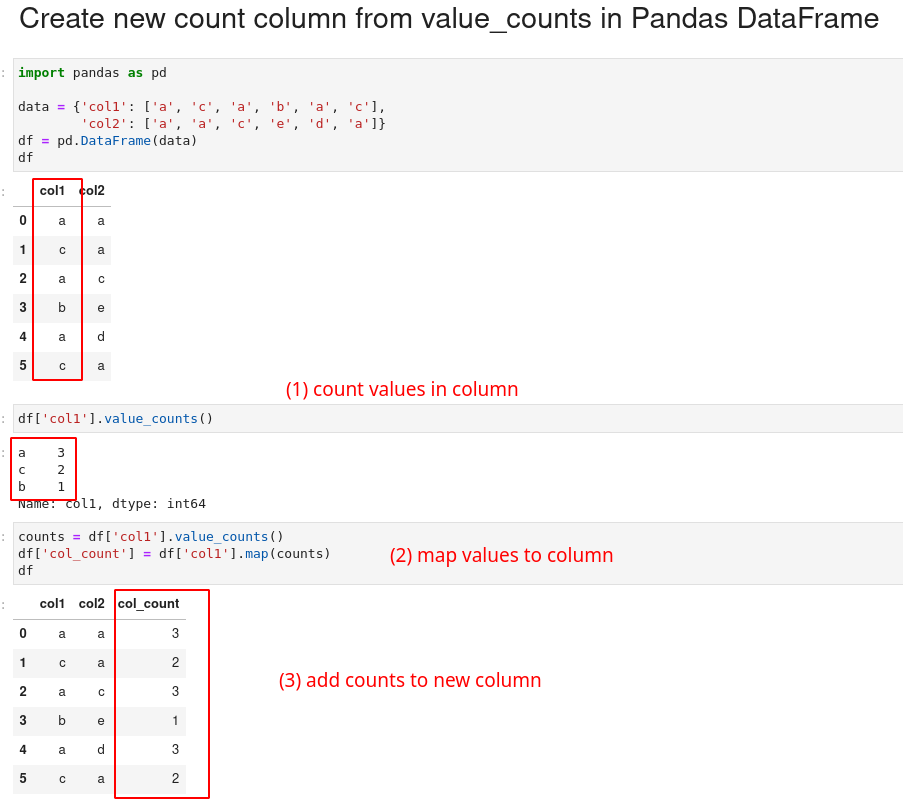
import pandas as pd
data = {'col1': ['a', 'c', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'c'],
'col2': ['x', 'y', 'z', 'x', 'x', 'y']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
DataFrame looks like:
| col1 | col2 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | a | a |
| 1 | c | a |
| 2 | a | c |
| 3 | b | e |
| 4 | a | d |
| 5 | c | b |
value_counts and map to column
I prefer to use value_counts and then map the counts to a given column. Finally we assign the values to new column:
counts = df['col1'].value_counts()
df['col_count'] = df['col1'].map(counts)
we can write the same in a single line:
df['col_count'] = df['col1'].map(df['col1'].value_counts())
result:
| col1 | col2 | col_count | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | a | a | 3 |
| 1 | c | a | 2 |
| 2 | a | c | 3 |
| 3 | b | e | 1 |
| 4 | a | d | 3 |
| 5 | c | b | 2 |
The advantage of this way is that we can map to different column and it's easier to read.
How does it work?
- the method
value_countscalculates the count of unique values in the columncol1. - next
mapfunction maps the values incol1to the corresponding count in the resulting Series. - the result is then assigned to a new column
col_countin the DataFrame.
Count and map to another column
We can count values in column col1 but map the values to column col2.
counts = df['col1'].value_counts()
df['col_count'] = df['col2'].map(counts)
This time count is mapped to col2 but the count is based on col1. This is very useful when we work with child-parent relationship:
| col1 | col2 | col_count | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | a | a | 3.0 |
| 1 | c | a | 3.0 |
| 2 | a | c | 2.0 |
| 3 | b | e | NaN |
| 4 | a | d | NaN |
| 5 | c | b | 1.0 |
group by and transform
In this section we will discuss how to add a counter per group in Pandas. We can group by one column, count and then transform the results to new column:
df['col_count'] = df.groupby(['col1'])['col1'].transform('count')
We get the same result as before:
| col1 | col2 | col_count | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | a | a | 3 |
| 1 | c | a | 2 |
| 2 | a | c | 3 |
| 3 | b | e | 1 |
| 4 | a | d | 3 |
| 5 | c | b | 2 |
Performance comparison
There's no difference in mid size DataFrames for both approaches:
df.groupby(['col1'])['col1'].transform('count')- 1.12 ms ± 15.2 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
df['col1'].value_counts();df['col_count'] = df['col1'].map(counts)- 1.15 ms ± 35.6 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
Tests were done with 6000 rows.
Conclusion
In this article, we saw how to use Pandas groupby and value_counts to add a new count column in DataFrame.
We also discussed how to count one column and map counts on another.