In this quick tutorial, we'll show how to export DataFrame to JSON format in Pandas. We will cover different export options.
(1) save DataFrame to a JSON file
df.to_json('file.json')
(2) change JSON format and data
df.to_json('file.json', orient='split')
Note: Read also: how to save Pandas DataFrame to JSON file without backslashes
There are multiple options for parameter orient of method - to_json:
split- dict{‘index’ -> [index], ‘columns’ -> [columns], ‘data’ -> [values]}
records- list[{column -> value}, … , {column -> value}]
index- dict{column -> {index -> value}}
columns- dict (default for DataFrame){column -> {index -> value}}
values- just the values array
table- dict{‘schema’: {schema}, ‘data’: {data}}
For Pandas Series several options are available for export to JSON
{‘split’, ‘records’, ‘index’, ‘table’}
Setup
Let's create a sample DataFrame which will be exported to a JSON file:
import pandas as pd
data = {'day': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
'temp': [9, 8, 6, 13, 10, 15, 9, 10],
'humidity': [0.89, 0.86, 0.54, 0.73, 0.45, 0.63, 0.95, 0.67]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data)
data looks like:
| day | temp | humidity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 9 | 0.89 |
| 1 | 2 | 8 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 3 | 6 | 0.54 |
| 3 | 4 | 13 | 0.73 |
| 4 | 5 | 10 | 0.45 |
1: Export DataFrame as JSON file
So let's start with the most simple example - exporting DataFrame as JSON string or a JSON file:
df.to_json('file.json')
If we provide the file name we will get a new JSON file created.
The output file path can be provided as relative path:
df.to_json(r'/home/json/file.json')
NaN’sand
Nonewill be converted to
nulland datetime objects will be converted to UNIX timestamps.
2: Export DataFrame as JSON string
Without file parameter - path_or_buf we will get JSON string:
df.to_json()
which will result into:
'{"day":{"0":1,"1":2,"2":3,"3":4,"4":5,"5":6,"6":7,"7":8},"temp":{"0":9,"1":8,"2":6,"3":13,"4":10,"5":15,"6":9,"7":10},"humidity":{"0":0.89,"1":0.86,"2":0.54,"3":0.73,"4":0.45,"5":0.63,"6":0.95,"7":0.67}}'
3: Export DataFrame as pretty JSON
Using parameter indent=True will prettify the JSON output of Pandas method to_json():
print(df.to_json(indent=True))
result:
{
"day":{
"0":1,
"1":2,
"2":3,
"3":4,
"4":5,
"5":6,
"6":7,
"7":8
},
"temp":{
"0":9,
"1":8,
"2":6,
"3":13,
"4":10,
"5":15,
"6":9,
"7":10
},
"humidity":{
"0":0.89,
"1":0.86,
"2":0.54,
"3":0.73,
"4":0.45,
"5":0.63,
"6":0.95,
"7":0.67
}
}
4: Export DataFrame JSON formats - orient
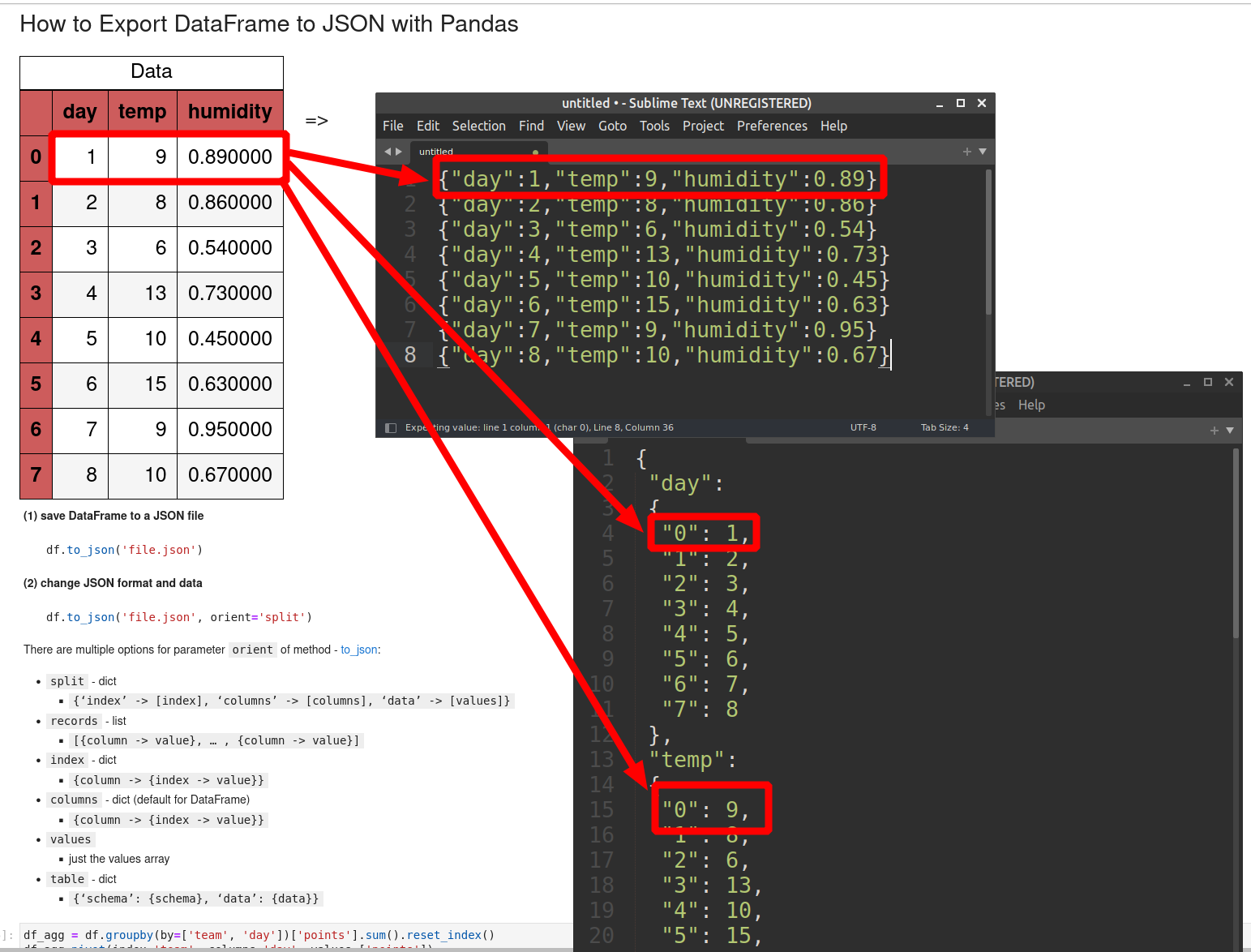
In this section we can see different JSON formats and data outputs.
4.1: columns - {column -> {index -> value}}
Let's start by the default export option for DataFrame - columns:
df.to_json()
is equivalent to df.to_json(orient='columns')
{"day":{"0":1,"1":2,"2":3,"3":4,"4":5,"5":6,"6":7,"7":8},
"temp":{"0":9,"1":8,"2":6,"3":13,"4":10,"5":15,"6":9,"7":10},
"humidity":{"0":0.89,"1":0.86,"2":0.54,"3":0.73,"4":0.45,"5":0.63,"6":0.95,"7":0.67}}
4.2: split - {‘index’ -> [index], ‘columns’ -> [columns], ‘data’ -> [values]}
Using orient with option split will give us:
df.to_json(orient='split')
JSON with keys - columns, index and data:
{"columns":["day","temp","humidity"],
"index":[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7],
"data":[[1,9,0.89],[2,8,0.86],[3,6,0.54],[4,13,0.73]..]}
4.3: records - [{column -> value}, … , {column -> value}]
For records we get list of dictionaries - each row as a new entry in the output JSON:
df.to_json(orient='records')
result:
[
{"day":1,"temp":9,"humidity":0.89},
{"day":2,"temp":8,"humidity":0.86},
{"day":3,"temp":6,"humidity":0.54},
{"day":4,"temp":13,"humidity":0.73},
{"day":5,"temp":10,"humidity":0.45}..]
4.4: index - {index -> {column -> value}}
With option index we got JSON file formatted as - index/data pairs:
df.to_json(orient='index')
result:
{"0":{"day":1,"temp":9,"humidity":0.89},
"1":{"day":2,"temp":8,"humidity":0.86},
"2":{"day":3,"temp":6,"humidity":0.54},
"3":{"day":4,"temp":13,"humidity":0.73},
"4":{"day":5,"temp":10,"humidity":0.45}..}
4.5: orient='values' <-> df.values
The option orient='values' is similar to df.values:
df.to_json(orient='values')
resulted JSON data is:
[[1,9,0.89],[2,8,0.86],[3,6,0.54],[4,13,0.73],[5,10,0.45],[6,15,0.63],[7,9,0.95],[8,10,0.67]]
4.6: table - {‘schema’: {schema}, ‘data’: {data}}
Finally we can use the option table. This give us DB like and JSON schema like JSON export of a DataFrame:
df.to_json(orient='table')
which results in next JSON schema:
{
"schema":
{
"fields":
[
{
"name": "index",
"type": "integer"
},
{
"name": "day",
"type": "integer"
},
{
"name": "temp",
"type": "integer"
},
{
"name": "humidity",
"type": "number"
}
],
"primaryKey":
[
"index"
],
"pandas_version": "1.4.0"
},
"data":
[
{
"index": 0,
"day": 1,
"temp": 9,
"humidity": 0.89
},
{
"index": 1,
"day": 2,
"temp": 8,
"humidity": 0.86
},
{
"index": 2,
"day": 3,
"temp": 6,
"humidity": 0.54
},
{
"index": 3,
"day": 4,
"temp": 13,
"humidity": 0.73
}
]
}
5: Export DataFrame as JSON lines
To save Pandas DataFrame as JSON lines we can use two parameters:
orient='records'lines=True
df.to_json(orient='records', lines=True)
this gives JSON line output:
{"day":1,"temp":9,"humidity":0.89}
{"day":2,"temp":8,"humidity":0.86}
{"day":3,"temp":6,"humidity":0.54}
{"day":4,"temp":13,"humidity":0.73}
Conclusion
In this article we saw how to export DataFrame as a JSON string of files. We show how to pretty print the JSON output.
We show different JSON formats and export to JSON lines.